Contents
- 1 Chlamydia during Pregnancy: Understanding the Risks, Recognizing Symptoms, and Exploring Treatment Options
- 1.1 Risks of Chlamydia during Pregnancy
- 1.2 Symptoms of Chlamydia during Pregnancy
- 1.3 FAQ about topic Chlamydia and Pregnancy Risks Symptoms and Treatment
- 1.3.1 What is chlamydia?
- 1.3.2 What are the risks of chlamydia during pregnancy?
- 1.3.3 What are the symptoms of chlamydia in pregnant women?
- 1.3.4 How is chlamydia diagnosed in pregnant women?
- 1.3.5 What is the treatment for chlamydia in pregnant women?
- 1.3.6 What is chlamydia?
- 1.3.7 How is chlamydia transmitted?
Chlamydia during Pregnancy: Understanding the Risks, Recognizing Symptoms, and Exploring Treatment Options

Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It can be passed from one person to another through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Chlamydia can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her baby during childbirth. This infection can lead to various complications for both the mother and the baby, making it important to understand the risks, symptoms, and treatment options.
When a pregnant woman is infected with chlamydia, it can increase the risk of premature birth, low birth weight, and even miscarriage. The infection can also be passed to the baby during delivery, leading to eye infections or pneumonia. Therefore, early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent these complications.
Screening for chlamydia is recommended for all pregnant women, especially those who are at high risk, such as those with multiple sexual partners or a history of sexually transmitted infections. It is usually done during the first prenatal visit and can be easily done through a urine test or a swab of the genital area. If a woman tests positive for chlamydia, prompt treatment with antibiotics is necessary to prevent the infection from spreading and causing harm to the mother and the baby.
Prevention is key when it comes to chlamydia and pregnancy. Practicing safe sex, including the use of condoms, can help reduce the risk of infection. It is also important for both partners to get tested and treated for chlamydia before engaging in sexual activity. Regular check-ups and screenings during pregnancy can help detect and treat any infections early on, ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Risks of Chlamydia during Pregnancy

Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection that can have serious consequences for pregnant women and their babies. It is important for pregnant women to be aware of the risks associated with chlamydia and take steps to prevent and treat the infection.
If left untreated, chlamydia can be transmitted from the mother to the baby during childbirth. This can lead to a number of complications, including pneumonia and eye infections in the newborn. In some cases, chlamydia can also cause premature birth or low birth weight.
The good news is that chlamydia can be easily treated with antibiotics. Pregnant women who are diagnosed with chlamydia should receive prompt treatment to reduce the risk of complications. It is important for pregnant women to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by their healthcare provider.
Prevention is key when it comes to chlamydia and pregnancy. Pregnant women should be screened for chlamydia early in their pregnancy, especially if they have a history of sexually transmitted infections or if their partner has been diagnosed with chlamydia. Screening can help identify and treat chlamydia before it causes any complications.
In addition to screening, pregnant women should also practice safe sex to reduce the risk of chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections. This includes using condoms consistently and correctly, and limiting the number of sexual partners.
Overall, it is important for pregnant women to be aware of the risks of chlamydia and take steps to prevent and treat the infection. By getting screened, practicing safe sex, and receiving prompt treatment, pregnant women can reduce the risk of complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Potential Complications
If left untreated, chlamydia infection during pregnancy can lead to several complications. It is important for pregnant women to receive timely screening and treatment for chlamydia to prevent these complications.
Untreated chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which is an infection of the reproductive organs. PID can lead to long-term complications such as chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
In addition, chlamydia infection during pregnancy can increase the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and neonatal conjunctivitis (pink eye) in the newborn. It can also be transmitted to the baby during delivery, leading to neonatal chlamydial infection.
The good news is that chlamydia can be easily treated with antibiotics. Pregnant women who test positive for chlamydia should receive prompt treatment to prevent complications. It is important for their sexual partners to be tested and treated as well to prevent reinfection.
Prevention is key in avoiding chlamydia complications during pregnancy. Practicing safe sex, including using condoms, can reduce the risk of chlamydia infection. Regular screening for chlamydia is also important, especially for pregnant women who are at higher risk.
In conclusion, chlamydia infection during pregnancy can lead to several complications if left untreated. Timely screening, treatment with antibiotics, and prevention measures can help reduce the risk of these complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Impact on the Baby

Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection that can have serious consequences for pregnant women and their babies. If left untreated, chlamydia can be passed from the mother to the baby during childbirth, leading to various complications.
One of the most common complications of chlamydia in newborns is conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye. This occurs when the infection is transmitted to the baby’s eyes during delivery. Conjunctivitis can cause redness, swelling, and discharge in the baby’s eyes, and if left untreated, it can lead to more serious eye problems.
In addition to conjunctivitis, chlamydia can also cause pneumonia in newborns. This occurs when the infection is transmitted to the baby’s lungs during delivery. Newborns with chlamydial pneumonia may experience symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. If left untreated, chlamydial pneumonia can lead to more severe respiratory problems.
It is important for pregnant women to undergo chlamydia screening during prenatal care to detect and treat any infections. If chlamydia is detected, it can be easily treated with antibiotics to prevent transmission to the baby. Treating chlamydia during pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
In conclusion, chlamydia can have a significant impact on the baby if left untreated during pregnancy. It is crucial for pregnant women to take preventive measures, such as practicing safe sex and getting regular screenings, to avoid chlamydia infection. If diagnosed with chlamydia, prompt treatment with antibiotics can help prevent transmission and reduce the risk of complications for the baby.
Symptoms of Chlamydia during Pregnancy

Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection that can be passed from an infected partner to a pregnant woman during sexual contact. It is important for pregnant women to be aware of the symptoms of chlamydia, as it can lead to complications if left untreated.
Some common symptoms of chlamydia during pregnancy include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Painful urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Bleeding between periods
- Rectal pain or discharge
It is important to note that many women with chlamydia do not experience any symptoms, which is why screening is crucial for early detection and treatment. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious complications during pregnancy, such as preterm birth, low birth weight, and even neonatal pneumonia or conjunctivitis.
If you suspect you may have chlamydia during pregnancy, it is important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can perform a simple screening test to diagnose the infection. Chlamydia can be easily treated with antibiotics, which are safe to use during pregnancy.
Prevention is key in avoiding chlamydia during pregnancy. Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and limiting sexual partners can help reduce the risk of transmission. Regular screening for chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections is also recommended, especially for pregnant women who are at a higher risk.
In conclusion, being aware of the symptoms of chlamydia during pregnancy is important for early detection and treatment. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to complications that can affect both the mother and the baby. Seeking medical attention, practicing safe sex, and regular screening can help prevent and manage chlamydia during pregnancy.
Common Signs
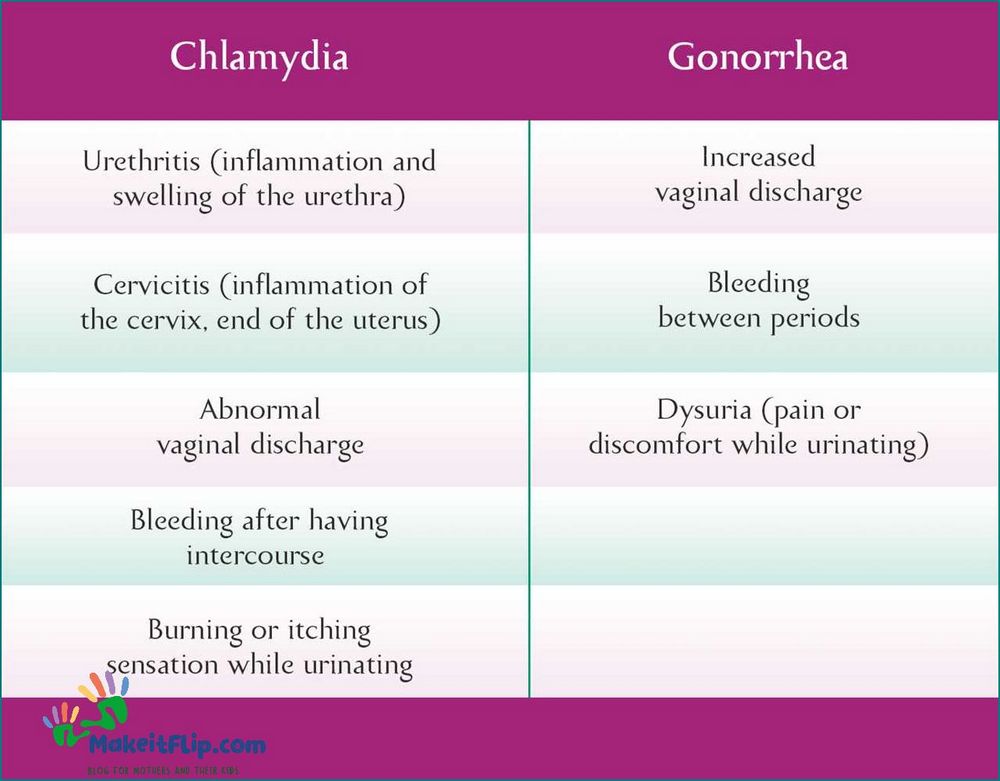
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection that can affect both men and women. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms, especially if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
In women, common signs of chlamydia include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Painful urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Lower abdominal pain
- Bleeding between periods
In men, common signs of chlamydia include:
- Clear or cloudy discharge from the penis
- Painful urination
- Swollen or tender testicles
If you experience any of these signs or symptoms, it is important to seek medical treatment as soon as possible. Chlamydia can lead to serious complications if left untreated, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and epididymitis in men.
Pregnant women with chlamydia can pass the infection to their baby during childbirth, which can lead to complications such as pneumonia or eye infections. It is important for pregnant women to get screened for chlamydia early in their pregnancy and receive prompt treatment if necessary.
The good news is that chlamydia can be easily treated with antibiotics. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your healthcare provider to ensure that the infection is completely cleared.
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of chlamydia. Practicing safe sex, using condoms consistently and correctly, and getting regular screenings if you are sexually active can help prevent the transmission of chlamydia.
Atypical Symptoms
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection that can be easily treated with antibiotics. However, it is important to be aware of the atypical symptoms that can occur, especially during pregnancy.
While many people with chlamydia experience symptoms such as genital discharge, pain during urination, and pelvic pain, some individuals may not have any noticeable symptoms at all. This is known as asymptomatic chlamydia.
During pregnancy, chlamydia can pose risks to both the mother and the baby. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to complications such as premature birth, low birth weight, and even miscarriage. It can also increase the risk of the baby developing chlamydia-related eye infections or pneumonia.
Because of the potential risks, it is important for pregnant women to undergo routine chlamydia screening. This involves a simple test that can detect the presence of the infection. If chlamydia is detected, it can be easily treated with antibiotics.
It is also important for pregnant women to inform their healthcare provider if they have had any recent sexual partners who may have had chlamydia. This information can help ensure that both the mother and the baby receive appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, while chlamydia may not always cause noticeable symptoms, it is important for pregnant women to be aware of the potential risks and to undergo routine screening. Early detection and treatment can help prevent complications and ensure the health of both the mother and the baby.
FAQ about topic Chlamydia and Pregnancy Risks Symptoms and Treatment
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
What are the risks of chlamydia during pregnancy?
Chlamydia during pregnancy can lead to complications such as preterm birth, low birth weight, and eye infections in the newborn. It can also be passed on to the baby during childbirth, which can cause pneumonia or a serious eye infection.
What are the symptoms of chlamydia in pregnant women?
Many pregnant women with chlamydia do not experience any symptoms. However, some may experience abnormal vaginal discharge, pain or burning during urination, and lower abdominal pain.
How is chlamydia diagnosed in pregnant women?
Chlamydia can be diagnosed through a urine test or a swab of the cervix or urethra. It is recommended that all pregnant women be screened for chlamydia during their first prenatal visit.
What is the treatment for chlamydia in pregnant women?
Chlamydia can be treated with antibiotics such as azithromycin or amoxicillin. It is important for pregnant women to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is completely cleared.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It can affect both men and women and can lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
How is chlamydia transmitted?
Chlamydia is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
I’m Diana Ricciardi, the author behind Makeitflip.com. My blog is a dedicated space for mothers and their kids, where I share valuable insights, tips, and information to make parenting a bit easier and more enjoyable.
From finding the best booster seat high chair for your child, understanding the connection between sciatica and hip pain, to exploring the benefits of pooping in relieving acid reflux, I cover a range of topics that are essential for every parent.
My goal is to provide you with practical advice and solutions that you can easily incorporate into your daily life, ensuring that you and your child have the best possible experience during these precious years.
