Contents
- 1 Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Purple Fingers: What You Need to Know
- 1.1 Causes of Purple Finger
- 1.2 Symptoms of Purple Finger
- 1.3 FAQ about topic Purple Finger Causes Symptoms and Treatment
- 1.3.1 What is purple finger?
- 1.3.2 What are the symptoms of purple finger?
- 1.3.3 What are the causes of purple finger?
- 1.3.4 How is purple finger diagnosed?
- 1.3.5 What is the treatment for purple finger?
- 1.3.6 What is purple finger?
- 1.3.7 What causes purple finger?
- 1.3.8 What are the symptoms of purple finger?
- 1.3.9 How is purple finger treated?
- 1.3.10 Can purple finger be prevented?
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Purple Fingers: What You Need to Know
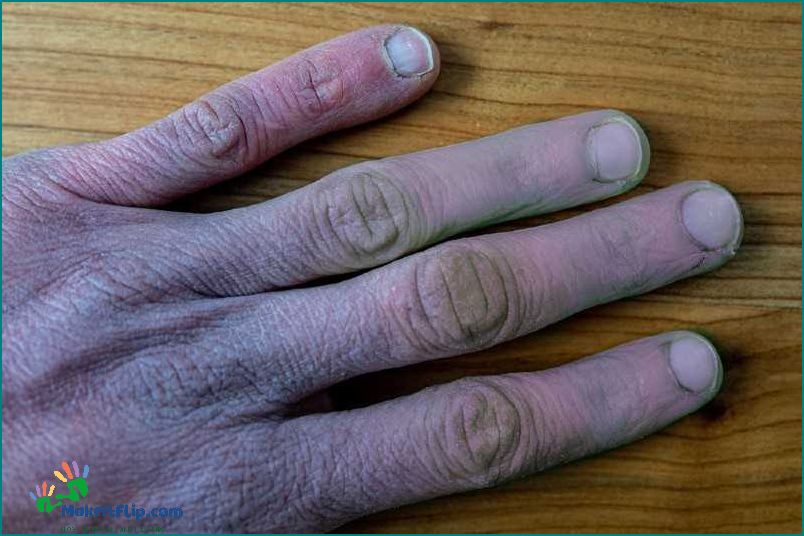
A purple finger, also known as violet finger, is a condition characterized by the discoloration of the skin on the finger, turning it a deep purple color. The discoloration occurs due to the presence of dye or other pigments in the skin. One of the common causes of purple finger is the use of grape juice or grape-flavored products, which contain natural pigments that can stain the skin.
People who work with dyes or pigments, such as painters or artists, may also develop purple fingers as a result of direct contact with these substances. Wearing gloves can help prevent the pigments from staining the skin, but if the gloves are not worn properly or are damaged, the fingers may still be affected.
In some cases, a purple finger may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Poor circulation, for example, can cause the fingers to turn purple due to a lack of oxygenated blood reaching the area. Other symptoms that may accompany a purple finger include numbness, tingling, or pain in the hand or finger.
Treatment for a purple finger depends on the underlying cause. If the discoloration is due to exposure to pigments or dyes, washing the affected area with soap and water may help remove the stain. If the discoloration persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Purple Finger
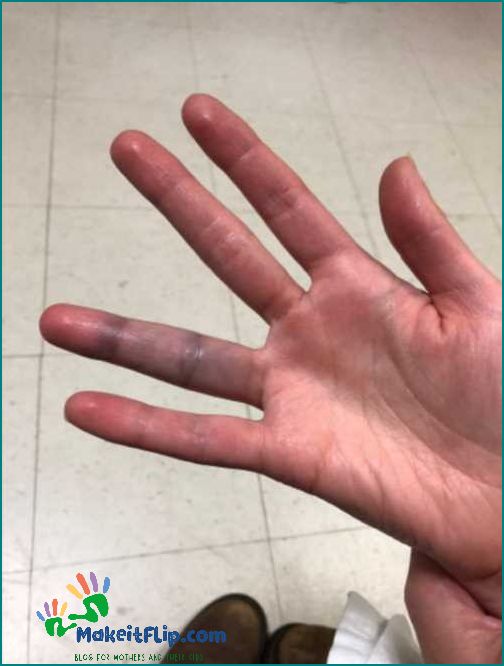

A purple finger can be caused by various factors, including:
- Wearing tight gloves or shoes that restrict blood flow to the fingers
- Staining the finger with a purple-colored substance, such as ink or dye
- An injury or trauma to the finger, resulting in bruising
- Raynaud’s disease, a condition that causes the blood vessels in the fingers to constrict, leading to a purple color
- Frostbite, which occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to extreme cold
- Peripheral artery disease, a condition that causes narrowed arteries and reduced blood flow to the extremities
If you notice a persistent purple color in your finger or hand without an obvious cause, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Trauma
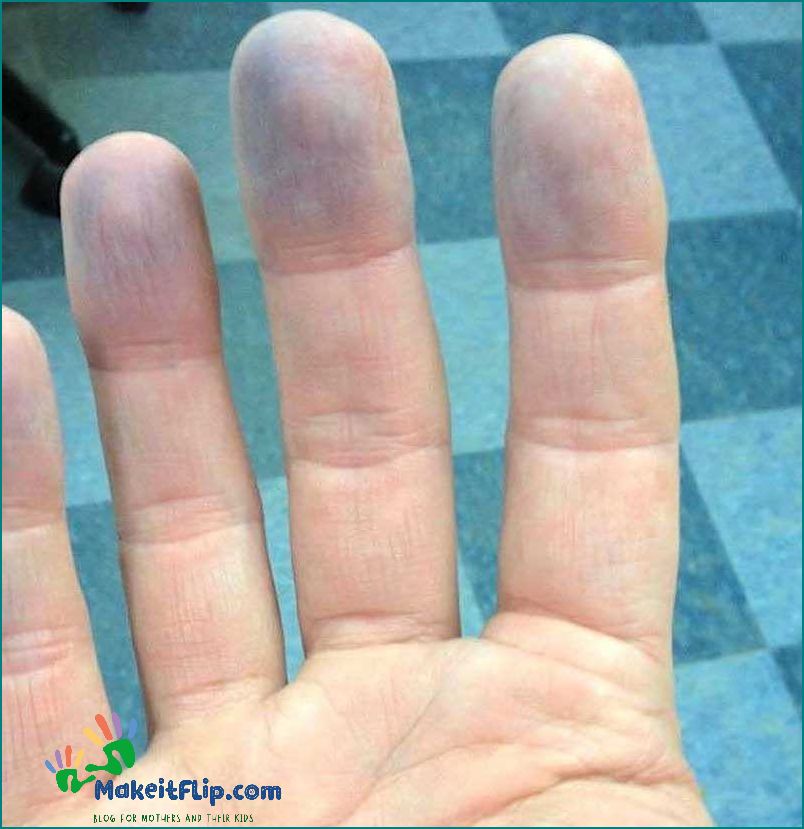
Trauma is one of the common causes of a purple finger. When the hand or finger experiences a forceful impact or injury, it can result in a violet or grape-like color. This discoloration occurs due to the rupture of blood vessels, causing blood to leak into the surrounding tissues. The blood acts as a stain or dye, giving the finger a purple hue.
If you have experienced trauma to your hand or finger and notice a purple color, it is important to seek medical attention. The healthcare provider will evaluate the extent of the injury and determine the appropriate treatment.
In some cases, the healthcare provider may recommend wearing gloves or using protective equipment to prevent further trauma. They may also suggest applying ice to reduce swelling and pain. It is important to follow their instructions and avoid any activities that may aggravate the injury.
Remember, the purple color is a sign of underlying damage and should not be ignored. Seeking prompt medical attention can help prevent complications and promote proper healing.
Raynaud’s Disease
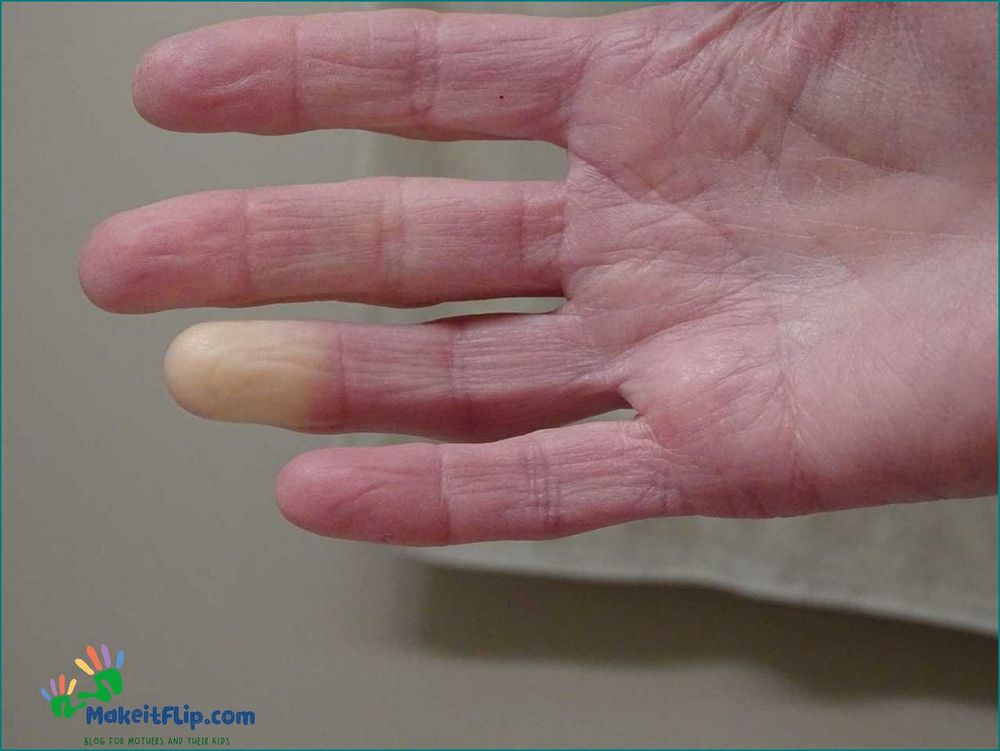
Raynaud’s Disease is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the fingers and toes, causing them to constrict and limit blood flow. This can result in a change in color of the affected areas, often turning them purple or violet.
The exact cause of Raynaud’s Disease is unknown, but it is believed to be related to abnormal blood vessel responses to cold temperatures or stress. When the blood vessels constrict, it reduces the amount of blood that can reach the fingers and toes, leading to the characteristic discoloration.
Symptoms of Raynaud’s Disease include fingers or toes that turn white, blue, or purple in response to cold or stress. The affected areas may also feel numb or cold to the touch. As blood flow returns, the fingers or toes may turn red and throb or tingle.
Treatment for Raynaud’s Disease focuses on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. This may include wearing warm gloves or mittens to protect the hands from cold temperatures, avoiding triggers such as exposure to cold or stress, and taking medications to improve blood flow.
If you suspect you may have Raynaud’s Disease, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They can help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend the best course of action to manage your condition.
Blood Clot
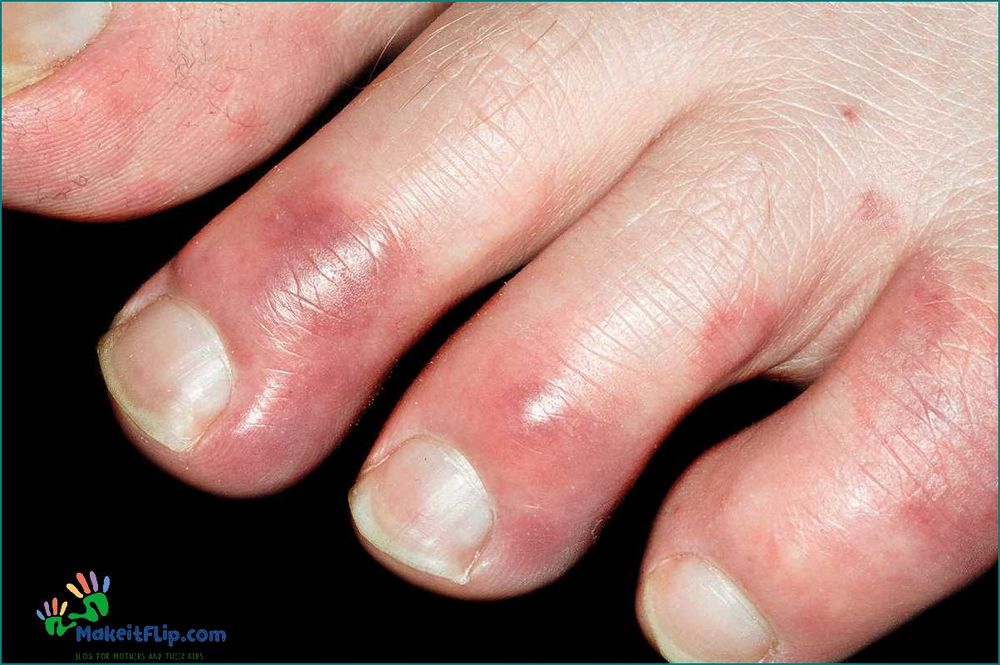
A blood clot, also known as a thrombus, is a gel-like mass formed by coagulated blood. It can occur in any part of the body, including the hand and finger. When a blood clot forms, it can cause the affected area to turn a deep shade of purple or violet, similar to the color of a grape stain.
Blood clots can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, surgery, or certain medical conditions. They can also occur as a result of prolonged immobility or poor circulation. In some cases, wearing tight gloves or jewelry on the hand or finger can contribute to the development of a blood clot.
Symptoms of a blood clot in the hand or finger may include swelling, pain, and warmth in the affected area. In severe cases, the finger or hand may become pale or numb. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a blood clot, as it can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Treatment for a blood clot in the hand or finger may involve medication to dissolve the clot, such as anticoagulants. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot. It is also important to address any underlying causes of the clot, such as treating an underlying medical condition or making lifestyle changes to improve circulation.
In conclusion, a blood clot in the hand or finger can cause the affected area to turn purple or violet in color. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a blood clot, as prompt treatment is necessary to prevent complications.
Symptoms of Purple Finger
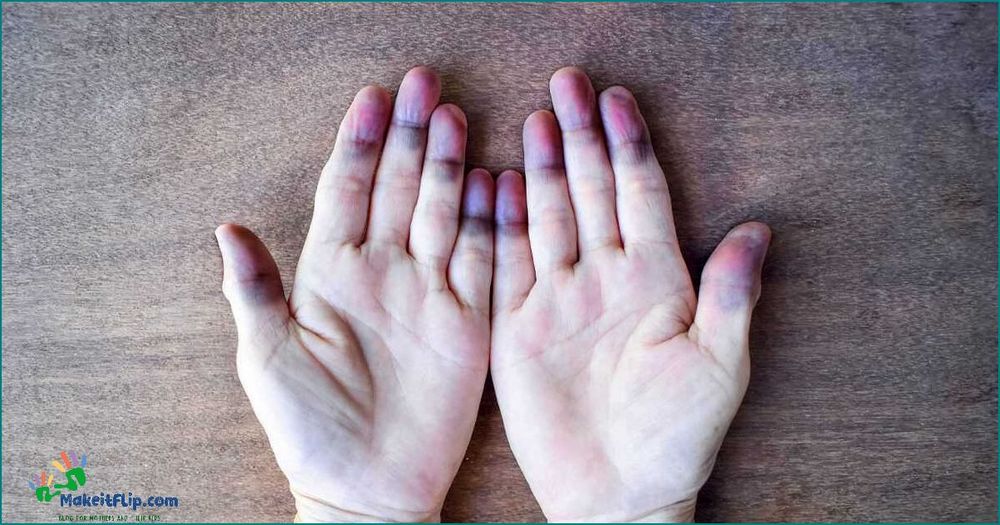
One of the main symptoms of a purple finger is the discoloration of the skin. The affected finger may turn a deep shade of purple, resembling the color of a grape or a violet.
In some cases, the purple color may be limited to certain areas of the finger, while in others, it may cover the entire finger. The intensity of the color may also vary, ranging from a light purple hue to a darker shade.
Individuals with a purple finger may also experience other symptoms such as pain, swelling, or numbness in the affected hand. These symptoms can be caused by various factors, including trauma, poor circulation, or an underlying medical condition.
If the purple color is caused by a dye or stain, it may be accompanied by a strong odor or a visible mark on the skin. In such cases, wearing gloves or using protective measures can help prevent the discoloration.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, as they may indicate a more serious underlying condition. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms and provide appropriate treatment to alleviate any discomfort or address the underlying cause of the purple finger.
FAQ about topic Purple Finger Causes Symptoms and Treatment
What is purple finger?
Purple finger is a condition characterized by the discoloration of the finger, which turns purple or bluish in color. It is usually caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood or poor circulation.
What are the symptoms of purple finger?
The symptoms of purple finger include a change in color of the finger to purple or bluish, numbness or tingling sensation, pain or discomfort, and swelling in the affected area.
What are the causes of purple finger?
The causes of purple finger can vary, but some common causes include Raynaud’s disease, frostbite, peripheral artery disease, blood clot, and trauma to the finger.
How is purple finger diagnosed?
Purple finger can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. They may also order additional tests such as blood tests, Doppler ultrasound, or angiography to determine the underlying cause.
What is the treatment for purple finger?
The treatment for purple finger depends on the underlying cause. It may include lifestyle changes such as keeping the hands warm, avoiding cold temperatures, and quitting smoking. Medications, such as vasodilators or blood thinners, may also be prescribed. In severe cases, surgery or other interventions may be necessary.
What is purple finger?
Purple finger is a condition characterized by the discoloration of the finger, turning it purple or bluish in color.
What causes purple finger?
Purple finger can be caused by various factors, such as poor circulation, trauma, Raynaud’s disease, frostbite, or certain medications.
What are the symptoms of purple finger?
The symptoms of purple finger may include discoloration of the finger, pain, swelling, numbness, and difficulty moving the finger.
How is purple finger treated?
The treatment for purple finger depends on the underlying cause. It may involve improving circulation, applying warm compresses, taking medications, or undergoing surgery in severe cases.
Can purple finger be prevented?
While it may not always be possible to prevent purple finger, there are certain measures that can help reduce the risk, such as keeping the hands warm, avoiding trauma to the fingers, and managing underlying conditions like Raynaud’s disease.
I’m Diana Ricciardi, the author behind Makeitflip.com. My blog is a dedicated space for mothers and their kids, where I share valuable insights, tips, and information to make parenting a bit easier and more enjoyable.
From finding the best booster seat high chair for your child, understanding the connection between sciatica and hip pain, to exploring the benefits of pooping in relieving acid reflux, I cover a range of topics that are essential for every parent.
My goal is to provide you with practical advice and solutions that you can easily incorporate into your daily life, ensuring that you and your child have the best possible experience during these precious years.
