Contents
- 1 Understanding the Highly Contagious Nature of Infectious Diseases: A Comprehensive Analysis
- 1.1 The Basics of Infectious Diseases
- 1.2 FAQ about topic So Contagious Understanding the Spread of Infectious Diseases
- 1.2.1 What are some common ways infectious diseases spread?
- 1.2.2 How can I protect myself from infectious diseases?
- 1.2.3 What are some examples of highly contagious infectious diseases?
- 1.2.4 Can infectious diseases be spread by animals?
- 1.2.5 How does the spread of infectious diseases impact public health?
- 1.2.6 What are some common infectious diseases?
- 1.2.7 How do infectious diseases spread?
- 1.2.8 What are the symptoms of infectious diseases?
- 1.2.9 How can we prevent the spread of infectious diseases?
- 1.2.10 What is the role of vaccines in preventing infectious diseases?
Understanding the Highly Contagious Nature of Infectious Diseases: A Comprehensive Analysis

Infectious diseases have always been a significant concern for humanity. From the Black Death to the Spanish Flu, these diseases have caused widespread devastation throughout history. What makes these diseases so dangerous is their ability to spread rapidly from person to person. Understanding the mechanisms behind their transmission is crucial in preventing and controlling outbreaks.
Contagiousness is a key factor in determining the severity of an infectious disease. Some diseases, like the common cold, are highly contagious and can easily be transmitted through respiratory droplets or direct contact. Others, like Ebola, are less contagious but have a higher fatality rate. The level of contagiousness depends on various factors, including the pathogen’s ability to survive outside the host and the ease with which it can enter a new host.
Transmission routes play a crucial role in the spread of infectious diseases. Respiratory diseases, such as COVID-19, can be transmitted through coughing, sneezing, or talking, as respiratory droplets containing the virus can be inhaled by others. Other diseases, like HIV, can be transmitted through sexual contact or sharing contaminated needles. Understanding these transmission routes is essential in implementing effective preventive measures.
“The key to controlling the spread of infectious diseases lies in early detection and prompt intervention.”
Prevention is the best defense against infectious diseases. Vaccination programs have been successful in eradicating diseases like smallpox and polio. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the spread of diseases. Quarantine measures and travel restrictions are also effective in containing outbreaks and preventing further transmission.
By understanding the contagiousness of infectious diseases and implementing preventive measures, we can minimize the impact of these diseases on individuals and communities. Public health efforts, such as surveillance systems and rapid response teams, are crucial in detecting and containing outbreaks before they become widespread. Together, we can work towards a healthier and safer future.
The Basics of Infectious Diseases
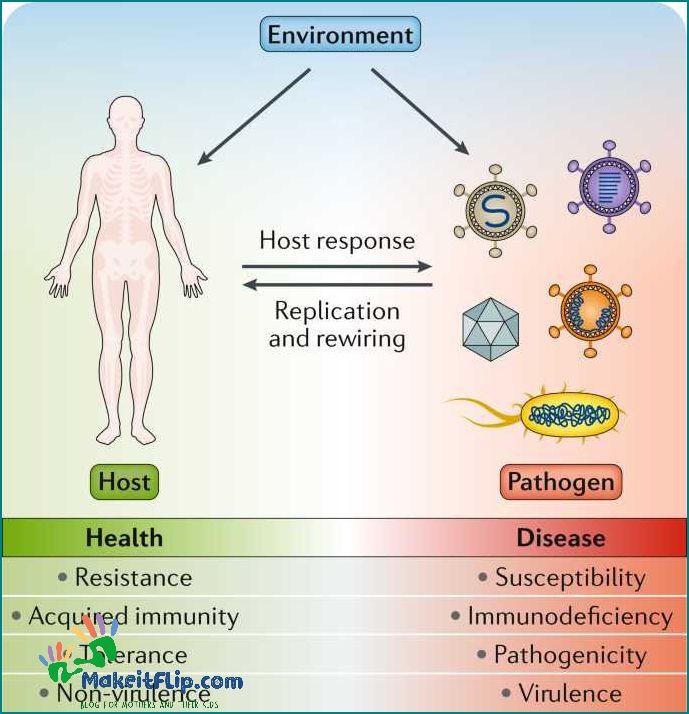
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. These microorganisms can spread from person to person, making them contagious. Understanding the basics of infectious diseases is crucial in preventing their spread and managing outbreaks.
Transmission: Contagious diseases can be transmitted through various routes, including direct contact with an infected person, inhalation of respiratory droplets, ingestion of contaminated food or water, or through vectors like mosquitoes or ticks.
Symptoms: The symptoms of infectious diseases can vary depending on the specific pathogen involved. Common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, fatigue, muscle aches, and gastrointestinal issues. Some infectious diseases may have more severe symptoms, leading to complications or even death.
Prevention: Preventing the spread of infectious diseases involves practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Vaccination is also a crucial preventive measure, as it helps to build immunity against specific diseases.
Treatment: Treatment for infectious diseases can vary depending on the specific pathogen involved. Antibiotics are commonly used to treat bacterial infections, while antiviral medications are used for viral infections. In some cases, supportive care, such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications, may be recommended to alleviate symptoms.
Outbreak Management: When an outbreak occurs, it is essential to implement measures to control and manage the spread of the disease. This may include isolation of infected individuals, contact tracing to identify and monitor potential cases, and public health interventions such as quarantine or travel restrictions.
Understanding the basics of infectious diseases is crucial in preventing their spread and protecting public health. By practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and following public health guidelines, we can help reduce the impact of contagious diseases on individuals and communities.
What are Infectious Diseases?

Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. These microorganisms can be easily transmitted from one person to another, making them contagious. Contagious diseases can spread through direct contact, such as touching or kissing an infected person, or through indirect contact, such as touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the microorganisms.
Common examples of infectious diseases include the flu, common cold, measles, chickenpox, tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, and COVID-19. These diseases can vary in severity and can affect different parts of the body, such as the respiratory system, digestive system, or bloodstream.
Contagious diseases can be transmitted through various routes, including respiratory droplets, blood, sexual contact, contaminated food or water, or insect bites. The transmission of these diseases can be prevented through measures such as practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, using condoms, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and maintaining a clean and sanitary environment.
Understanding the spread of infectious diseases is crucial for public health officials and healthcare professionals in order to develop effective prevention and control strategies. By studying the transmission patterns and risk factors associated with contagious diseases, scientists can develop vaccines, antiviral medications, and other interventions to reduce the impact of these diseases on individuals and communities.
Overall, infectious diseases pose a significant threat to global health, and it is important for individuals to be aware of the risks and take appropriate measures to protect themselves and others from these contagious illnesses.
How Do Infectious Diseases Spread?
Infectious diseases can spread in various ways, but the most common method is through direct contact with an infected person or object. When a person who is contagious comes into contact with others, they can easily transmit the disease.
Respiratory diseases, such as the flu or common cold, are often spread through droplets in the air. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets containing the virus or bacteria can be inhaled by others nearby, leading to infection.
Some diseases can also be spread through contact with bodily fluids, such as blood or saliva. This can occur through activities such as sharing needles or engaging in unprotected sexual contact. It is important to practice safe behaviors to prevent the spread of these diseases.
In addition to direct contact, infectious diseases can also be spread through indirect contact. This can happen when a person touches a contaminated surface, such as a doorknob or countertop, and then touches their face or mouth. Proper hygiene, including regular handwashing, can help reduce the risk of spreading these diseases.
Vector-borne diseases, such as malaria or Lyme disease, are spread through the bites of infected insects or animals. These diseases are commonly transmitted by mosquitoes, ticks, or fleas. Taking precautions to avoid being bitten, such as using insect repellent or wearing protective clothing, can help prevent the spread of these diseases.
It is important to note that not all infectious diseases are contagious. Some diseases, such as tetanus or botulism, are caused by toxins rather than living organisms and cannot be spread from person to person.
Understanding how infectious diseases spread is crucial in preventing their transmission. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals or objects, and taking appropriate precautions, we can help reduce the spread of contagious diseases and protect ourselves and others.
The Role of Pathogens in Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms called pathogens. These pathogens can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. They have the ability to invade the body and cause infection, leading to various symptoms and health complications.
Pathogens are highly specialized organisms that have evolved to survive and thrive in specific environments, including the human body. They are capable of evading the immune system and multiplying rapidly, spreading from person to person and causing widespread outbreaks.
Pathogens can enter the body through various routes, such as inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces. Once inside the body, they can invade cells, tissues, and organs, disrupting normal bodily functions and causing damage.
Some pathogens produce toxins that can further harm the body. These toxins can cause inflammation, tissue damage, and organ failure. In severe cases, they can even be life-threatening.
Each pathogen has its own unique characteristics and mechanisms of infection. For example, viruses are tiny particles that can only replicate inside host cells. They hijack the host’s cellular machinery to produce more viruses, eventually causing cell death and the release of new viral particles.
Bacteria, on the other hand, are single-celled organisms that can reproduce independently. They can produce toxins or invade tissues directly, causing damage and triggering an immune response. Fungi and parasites have their own distinct ways of infecting and causing disease as well.
Understanding the role of pathogens in infectious diseases is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By studying their mechanisms of infection, scientists can identify potential targets for drugs and vaccines. They can also develop diagnostic tools to detect and identify pathogens quickly, enabling early intervention and containment of outbreaks.
So, pathogens play a central role in the spread and severity of infectious diseases. By understanding their biology and behavior, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from the threat of these diseases.
FAQ about topic So Contagious Understanding the Spread of Infectious Diseases
What are some common ways infectious diseases spread?
Some common ways infectious diseases spread include direct contact with an infected person, respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing, contaminated food or water, and contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
How can I protect myself from infectious diseases?
To protect yourself from infectious diseases, it is important to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently with soap and water, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and keeping your vaccinations up to date.
What are some examples of highly contagious infectious diseases?
Some examples of highly contagious infectious diseases include measles, chickenpox, influenza, and tuberculosis.
Can infectious diseases be spread by animals?
Yes, infectious diseases can be spread by animals. For example, diseases like rabies and Lyme disease can be transmitted to humans through bites from infected animals.
How does the spread of infectious diseases impact public health?
The spread of infectious diseases can have a significant impact on public health. It can lead to outbreaks and epidemics, strain healthcare systems, and cause economic losses. Public health measures, such as surveillance, prevention, and control strategies, are implemented to mitigate the spread of infectious diseases and protect the population.
What are some common infectious diseases?
Some common infectious diseases include the flu, common cold, tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, and hepatitis.
How do infectious diseases spread?
Infectious diseases can spread through various means, such as direct contact with an infected person or their bodily fluids, airborne transmission through respiratory droplets, ingestion of contaminated food or water, or through vectors like mosquitoes or ticks.
What are the symptoms of infectious diseases?
The symptoms of infectious diseases can vary depending on the specific disease, but common symptoms include fever, fatigue, coughing, sneezing, sore throat, muscle aches, and diarrhea.
How can we prevent the spread of infectious diseases?
We can prevent the spread of infectious diseases by practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, covering mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, getting vaccinated, and following proper food safety measures.
What is the role of vaccines in preventing infectious diseases?
Vaccines play a crucial role in preventing infectious diseases by stimulating the immune system to produce an immune response against specific pathogens. This helps the body recognize and fight off the pathogens more effectively, reducing the risk of infection and transmission.
I’m Diana Ricciardi, the author behind Makeitflip.com. My blog is a dedicated space for mothers and their kids, where I share valuable insights, tips, and information to make parenting a bit easier and more enjoyable.
From finding the best booster seat high chair for your child, understanding the connection between sciatica and hip pain, to exploring the benefits of pooping in relieving acid reflux, I cover a range of topics that are essential for every parent.
My goal is to provide you with practical advice and solutions that you can easily incorporate into your daily life, ensuring that you and your child have the best possible experience during these precious years.
