Contents
- 1 Exploring the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for Abdominal Separation: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 Causes of Abdominal Separation
- 1.2 Symptoms of Abdominal Separation
- 1.3 FAQ about topic Understanding Abdominal Separation Causes Symptoms and Treatment
- 1.3.1 What is abdominal separation?
- 1.3.2 What are the causes of abdominal separation?
- 1.3.3 What are the symptoms of abdominal separation?
- 1.3.4 How is abdominal separation diagnosed?
- 1.3.5 What are the treatment options for abdominal separation?
- 1.3.6 What is abdominal separation?
- 1.3.7 What causes abdominal separation?
- 1.3.8 What are the symptoms of abdominal separation?
- 1.3.9 Can abdominal separation be treated without surgery?
- 1.3.10 When should I consider surgery for abdominal separation?
Exploring the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for Abdominal Separation: A Comprehensive Guide
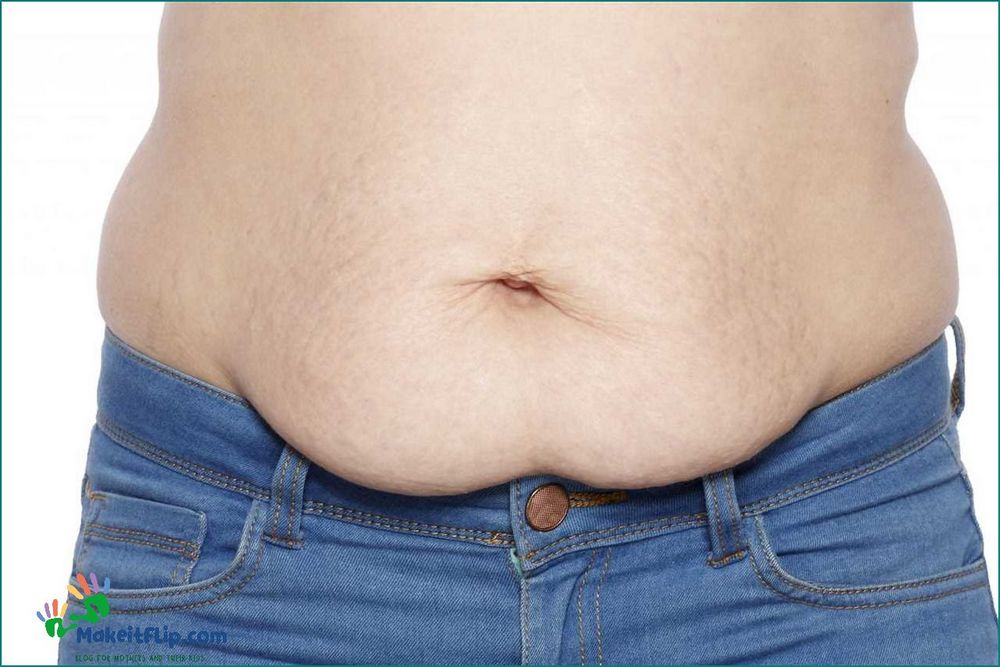

Abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, is a condition that occurs when the muscles of the abdomen separate during pregnancy or postpartum. This separation can cause a variety of symptoms and can affect the core muscles, which are essential for stability and movement.
During pregnancy, the growing uterus puts pressure on the abdominal muscles, causing them to stretch and weaken. This can lead to a separation of the rectus muscles, which run vertically down the front of the abdomen. Postpartum, the muscles may struggle to regain their strength and return to their pre-pregnancy position, resulting in a persistent separation.
Common symptoms of abdominal separation include a bulge or ridge in the midline of the abdomen, lower back pain, and difficulty with core exercises. It is important to note that not all women who have had children will experience abdominal separation, and it can also occur in men and individuals who have never been pregnant.
Treatment for abdominal separation typically involves exercises that focus on strengthening the core muscles and closing the gap between the separated muscles. Physical therapy, targeted exercises, and wearing a support garment can all be effective in improving muscle tone and reducing the separation. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the abdominal muscles.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for abdominal separation is important for both pregnant and postpartum individuals, as well as anyone experiencing core muscle weakness. By addressing this condition early on, individuals can work towards improving muscle strength and function, leading to better overall health and well-being.
Causes of Abdominal Separation
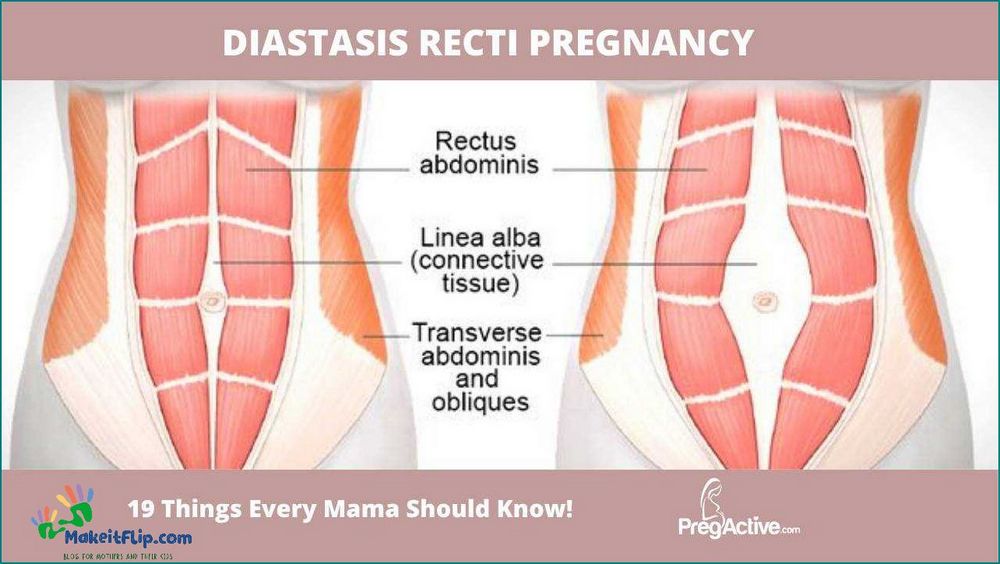
Abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, is a condition that occurs when the rectus abdominis muscles, commonly referred to as the “six-pack” muscles, separate along the midline of the abdomen. This separation can happen for various reasons, including:
Pregnancy: Abdominal separation is most commonly associated with pregnancy. As the uterus expands to accommodate the growing baby, the abdominal muscles stretch and can weaken, leading to separation.
Postpartum: After giving birth, the abdominal muscles may not fully recover and return to their pre-pregnancy state. This can result in a persistent separation that may require treatment.
Improper exercise: Engaging in certain exercises or movements that put excessive strain on the core muscles can contribute to abdominal separation. This includes exercises that involve heavy lifting, improper form, or repetitive movements that place excessive pressure on the abdominal area.
Weak core muscles: Weakness in the core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, can increase the risk of abdominal separation. This can be due to factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, lack of exercise, or inadequate muscle conditioning.
Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to abdominal separation, making them more prone to developing the condition. This can be influenced by factors such as collagen structure and tissue elasticity.
Other factors: Certain medical conditions, such as obesity, multiple pregnancies, or abdominal surgeries, can also contribute to abdominal separation.
It is important to note that abdominal separation can vary in severity and may not always cause noticeable symptoms. However, if you suspect you have abdominal separation, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Pregnancy
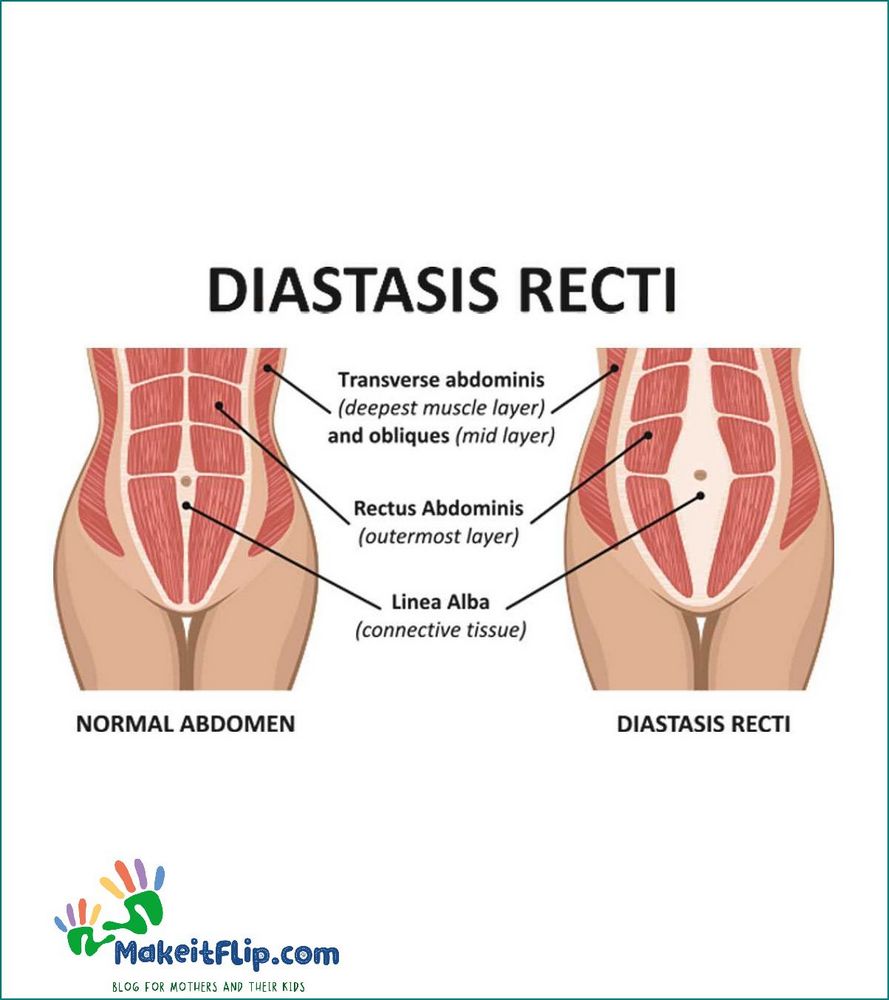
Pregnancy is one of the main causes of abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti. During pregnancy, the growing uterus puts pressure on the abdominal muscles, causing them to stretch and separate. This separation occurs in the linea alba, the connective tissue that runs down the center of the abdomen.
The core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, play a crucial role in supporting the abdomen and maintaining stability. However, during pregnancy, the hormones relaxin and progesterone are released, which loosen the ligaments and connective tissues in the body. This hormonal change, combined with the pressure from the growing baby, can weaken the core muscles and lead to diastasis recti.
Diastasis recti is common during pregnancy, with studies suggesting that it affects up to two-thirds of pregnant women. It can cause symptoms such as a visible bulge or “doming” in the abdomen, lower back pain, and difficulty with core strength and stability.
After pregnancy, it is important to address diastasis recti to prevent long-term complications. Postpartum exercises and physical therapy can help strengthen the core muscles and promote healing of the abdominal separation. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Excessive Weightlifting
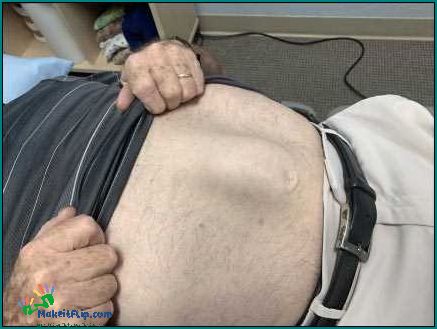
Excessive weightlifting can contribute to abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti. This condition is not limited to postpartum women; it can also affect individuals who engage in heavy weightlifting or other activities that put excessive strain on the abdominal muscles.
When you lift heavy weights, especially without proper form and technique, it can cause the muscles in your abdomen to separate. This separation occurs when the connective tissue between the rectus muscles, which run vertically down the abdomen, becomes stretched and weakened.
Weightlifting can exacerbate an existing abdominal separation or even cause one to develop. The repetitive strain and pressure placed on the core muscles during weightlifting can further weaken the connective tissue, leading to a wider separation.
It is important to note that weightlifting alone may not cause abdominal separation. Factors such as genetics, pregnancy, and previous abdominal surgeries can also contribute to the development of this condition. However, excessive weightlifting can increase the risk and severity of abdominal separation.
If you are experiencing symptoms of abdominal separation, such as a bulging or doming abdomen, lower back pain, or difficulty engaging your core muscles, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can assess the extent of your separation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Treatment for abdominal separation caused by excessive weightlifting may include exercises to strengthen the core muscles, such as pelvic tilts, planks, and modified abdominal exercises. It is crucial to perform these exercises under the guidance of a qualified fitness professional or physical therapist to ensure proper form and avoid further injury.
In addition to targeted exercises, it is essential to modify your weightlifting routine to prevent further strain on the abdominal muscles. This may involve reducing the amount of weight lifted, focusing on proper form and technique, and incorporating exercises that engage the entire core rather than solely targeting the rectus muscles.
Overall, excessive weightlifting can contribute to abdominal separation, particularly in individuals who already have weakened or stretched abdominal muscles. It is important to listen to your body, seek medical advice if you experience symptoms, and modify your exercise routine to prevent further damage to the core muscles.
Abdominal Trauma

Abdominal trauma refers to any injury or damage to the abdomen, which is the area between the chest and the pelvis. This type of trauma can cause various complications, including abdominal separation or diastasis recti.
Abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, is a condition in which the muscles of the abdomen separate or move apart. This can occur due to various factors, including trauma to the abdominal area. Abdominal trauma can result from accidents, falls, or direct blows to the abdomen.
When the abdominal muscles separate, it can lead to a weakened core and affect the stability of the body. This can make it difficult to perform certain exercises or movements that require core strength. Postpartum women are particularly susceptible to abdominal separation due to the stretching and weakening of the abdominal muscles during pregnancy.
Common symptoms of abdominal separation include a bulging or protruding abdomen, lower back pain, and difficulty engaging the core muscles. In severe cases, a visible gap or indentation may be present in the midline of the abdomen.
Treatment for abdominal separation typically involves exercises that target the core muscles and help to strengthen and realign the abdominal muscles. These exercises may include pelvic tilts, abdominal compressions, and modified planks. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a physical therapist for a personalized treatment plan.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair severe abdominal separation. This is usually considered when conservative treatments have been ineffective or when the separation is causing significant functional impairments.
Overall, abdominal trauma can lead to abdominal separation or diastasis recti, which can affect core strength and stability. It is important to seek appropriate medical care and follow a tailored treatment plan to address the condition and improve abdominal muscle function.
Symptoms of Abdominal Separation
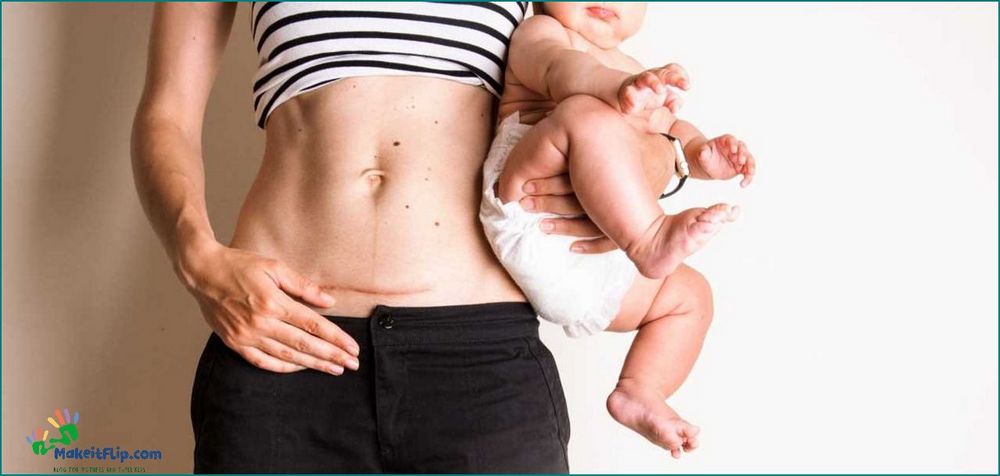

Abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, is a common condition that occurs during pregnancy or postpartum. It is characterized by the separation of the abdominal muscles, specifically the rectus muscles, which form the core of the body.
One of the main symptoms of abdominal separation is a visible bulge or protrusion in the midline of the abdomen. This bulge is often more pronounced when the person is standing or contracting their abdominal muscles. It can be mistaken for a persistent “baby bump” even after pregnancy.
In addition to the visible bulge, individuals with abdominal separation may also experience back pain, pelvic floor dysfunction, and poor posture. The weakened core muscles can lead to difficulties in performing everyday tasks and exercises that require core strength.
During exercise, individuals with abdominal separation may notice a gap or hollowing in the midline of their abdomen. This can be felt by placing fingers in the midline and contracting the abdominal muscles. The gap may be wide or narrow, depending on the severity of the separation.
It is important to note that not all individuals with abdominal separation experience symptoms. Some may have a mild separation that does not cause any discomfort or functional limitations. However, it is still recommended to seek medical advice if you suspect you have abdominal separation, especially if you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above.
FAQ about topic Understanding Abdominal Separation Causes Symptoms and Treatment
What is abdominal separation?
Abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, is a condition where the abdominal muscles separate or move apart. This can happen during pregnancy or due to excessive strain on the abdominal muscles.
What are the causes of abdominal separation?
Abdominal separation can be caused by pregnancy, obesity, improper lifting techniques, and excessive abdominal exercises. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can weaken the connective tissues, leading to separation of the abdominal muscles.
What are the symptoms of abdominal separation?
The symptoms of abdominal separation include a visible bulge or protrusion in the abdomen, lower back pain, weak abdominal muscles, and difficulty in performing certain movements. Some individuals may also experience digestive issues and urinary incontinence.
How is abdominal separation diagnosed?
Abdominal separation can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. The separation is measured by checking the gap between the abdominal muscles. Imaging tests such as ultrasound may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for abdominal separation?
Treatment options for abdominal separation include physical therapy exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles, wearing a support garment or binder, and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the abdominal muscles. In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair the separated muscles.
What is abdominal separation?
Abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, is a condition where the abdominal muscles separate due to the stretching of the connective tissue between them.
What causes abdominal separation?
Abdominal separation can be caused by pregnancy, obesity, weightlifting, and excessive abdominal exercises. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can weaken the connective tissue, leading to separation of the muscles.
What are the symptoms of abdominal separation?
The symptoms of abdominal separation include a bulge or ridge in the middle of the abdomen, lower back pain, and a weak core. Some people may also experience urinary incontinence and difficulty with certain movements.
Can abdominal separation be treated without surgery?
Yes, abdominal separation can be treated without surgery. Physical therapy exercises, such as pelvic tilts, abdominal bracing, and kegel exercises, can help strengthen the abdominal muscles and reduce the separation. Wearing a supportive abdominal binder or splint may also be recommended.
When should I consider surgery for abdominal separation?
Surgery for abdominal separation is usually considered as a last resort when conservative treatments have failed. It may be recommended if the separation is severe, causing significant functional limitations or pain. It is best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if surgery is necessary in your case.
I’m Diana Ricciardi, the author behind Makeitflip.com. My blog is a dedicated space for mothers and their kids, where I share valuable insights, tips, and information to make parenting a bit easier and more enjoyable.
From finding the best booster seat high chair for your child, understanding the connection between sciatica and hip pain, to exploring the benefits of pooping in relieving acid reflux, I cover a range of topics that are essential for every parent.
My goal is to provide you with practical advice and solutions that you can easily incorporate into your daily life, ensuring that you and your child have the best possible experience during these precious years.
