Contents
- 1 Exploring the Impact of Low Progesterone Levels on Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Analysis
- 1.1 What is Progesterone?
- 1.2 Effects of Low Progesterone in Pregnancy
- 1.3 FAQ about topic Understanding the Effects of Low Progesterone in Pregnancy
- 1.3.1 What is progesterone and why is it important during pregnancy?
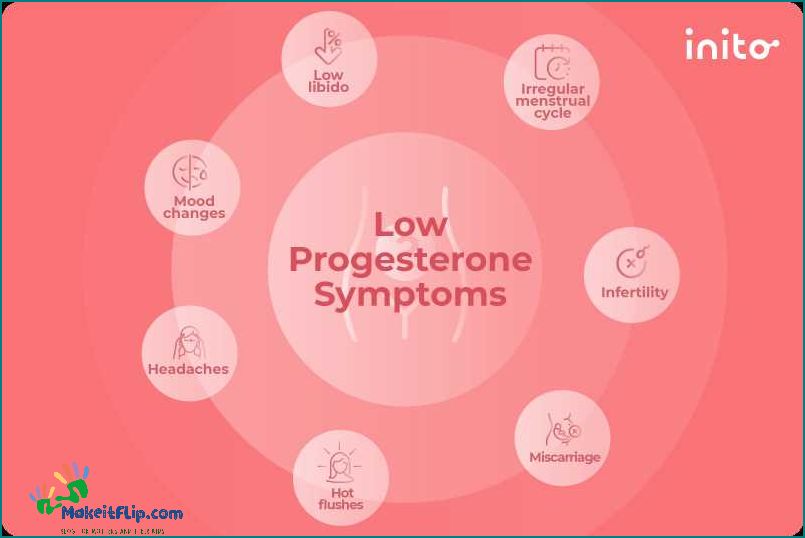
- 1.3.2 What are the symptoms of low progesterone in pregnancy?
- 1.3.3 How is low progesterone in pregnancy diagnosed?
- 1.3.4 Can low progesterone in pregnancy be treated?
- 1.3.5 What are the possible complications of low progesterone in pregnancy?
- 1.3.6 What are the effects of low progesterone in pregnancy?
Exploring the Impact of Low Progesterone Levels on Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Analysis
Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in pregnancy. It is responsible for preparing the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg and maintaining the pregnancy. However, some women may experience low levels of progesterone, which can have significant effects on their fertility and pregnancy.
Low progesterone levels can lead to a variety of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, difficulty getting pregnant, and recurrent miscarriages. These symptoms can be distressing for women who are trying to conceive or who have experienced the loss of a pregnancy.
Treatment for low progesterone levels in pregnancy may involve hormone supplementation. This can help to support the pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage. It is important for women who suspect they may have low progesterone levels to speak with their healthcare provider, who can perform tests to determine their hormone levels and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Understanding the effects of low progesterone in pregnancy is essential for women who are trying to conceive or who are already pregnant. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment, women can improve their chances of a successful pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications such as miscarriage.
What is Progesterone?
Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in fertility and pregnancy. It is produced by the ovaries in women and the testes in men, but its main function is to prepare the uterus for pregnancy and support the development of the fetus.
During a normal menstrual cycle, progesterone levels rise after ovulation and help prepare the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy occurs, progesterone levels continue to rise and play a vital role in maintaining the pregnancy.
Low progesterone levels can have various symptoms and effects on pregnancy. Some common symptoms of low progesterone include irregular menstrual cycles, spotting or bleeding during pregnancy, and recurrent miscarriages.
Low progesterone levels can also increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as preterm birth and preeclampsia. It can also affect the development of the fetus, leading to growth restrictions or birth defects.
Treatment for low progesterone levels in pregnancy may include hormonal supplementation, such as progesterone injections or vaginal suppositories. These treatments can help support the pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
In conclusion, progesterone is a crucial hormone for fertility and pregnancy. Low progesterone levels can have various symptoms and effects on pregnancy, but with proper treatment, the risks can be minimized, and a healthy pregnancy can be achieved.
Importance of Progesterone in Pregnancy
Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in pregnancy. It is produced by the ovaries and the placenta, and its levels are highest during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Progesterone helps to prepare the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg and supports the growth and development of the fetus.
Low levels of progesterone during pregnancy can have significant consequences. One of the main risks is an increased likelihood of miscarriage. Progesterone helps to maintain the uterine lining and prevent it from shedding, which is necessary for a healthy pregnancy. When progesterone levels are low, the uterine lining may not be able to support the implantation and growth of the embryo, leading to a miscarriage.
In addition to its role in maintaining the uterine lining, progesterone also helps to regulate other hormones involved in fertility and pregnancy. It works in conjunction with estrogen to prepare the breasts for milk production and helps to prevent contractions of the uterus during early pregnancy. Progesterone also plays a role in the development of the placenta, which is essential for providing nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
Low progesterone levels in pregnancy can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, mood swings, and breast tenderness. Some women may also experience spotting or bleeding. If you suspect that you have low progesterone levels during pregnancy, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for low progesterone levels in pregnancy may involve hormone supplementation. This can be done through oral medications, injections, or vaginal suppositories. By increasing progesterone levels, these treatments can help to support a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
In conclusion, progesterone plays a vital role in pregnancy by supporting the implantation and growth of the fetus, maintaining the uterine lining, regulating other hormones, and supporting the development of the placenta. Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage and cause various symptoms. If you suspect low progesterone levels, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Role of Progesterone in Maintaining Pregnancy
Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy. It is produced by the ovaries and helps prepare the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg. Once pregnancy is established, progesterone continues to be produced by the placenta to support the growing fetus.
Low levels of progesterone can lead to complications in pregnancy, including an increased risk of miscarriage. Progesterone helps to maintain the lining of the uterus, which is essential for a healthy pregnancy. When progesterone levels are low, the lining may not be able to support the implantation and growth of the embryo, leading to a miscarriage.
Some common symptoms of low progesterone in pregnancy include spotting or bleeding, cramping, and a decrease in pregnancy symptoms. These symptoms may indicate a hormonal imbalance and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Treatment for low progesterone in pregnancy may involve progesterone supplementation. This can be done through oral medication, vaginal suppositories, or injections. By increasing progesterone levels, the risk of miscarriage can be reduced, and the pregnancy can be supported.
Progesterone also plays a role in fertility. It helps regulate the menstrual cycle and prepares the uterus for pregnancy. Women with low progesterone levels may have difficulty getting pregnant or maintaining a pregnancy. In these cases, fertility treatments may be recommended to help increase progesterone levels and improve the chances of conception.
| Low Progesterone Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Spotting or bleeding | Progesterone supplementation |
| Cramping | Oral medication |
| Decrease in pregnancy symptoms | Vaginal suppositories |
In conclusion, progesterone plays a vital role in maintaining pregnancy. Low levels of progesterone can lead to complications such as miscarriage, but with appropriate treatment, the risk can be reduced. It is important for pregnant women to be aware of the symptoms of low progesterone and to seek medical advice if they experience any concerning symptoms.
Effects of Low Progesterone in Pregnancy

Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in pregnancy. It helps to prepare the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg and supports the growth and development of the placenta. Low levels of progesterone during pregnancy can have various effects on both the mother and the developing baby.
One of the main effects of low progesterone in pregnancy is a decreased fertility. Progesterone is essential for maintaining a healthy pregnancy, and low levels of this hormone can make it difficult for a woman to conceive. Women with low progesterone may experience irregular menstrual cycles and have difficulty getting pregnant.
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can also lead to symptoms such as spotting or bleeding, abdominal pain, and cramping. These symptoms can be signs of a threatened miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy, which is a pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus. It is important for women experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
In some cases, low progesterone levels can increase the risk of miscarriage. Progesterone helps to maintain the lining of the uterus and support the developing embryo. When progesterone levels are low, the uterus may not be able to support the pregnancy, leading to a miscarriage. Women who have a history of recurrent miscarriages may be prescribed progesterone supplements to help prevent future pregnancy losses.
Treatment for low progesterone during pregnancy may involve progesterone supplementation. This can be done through oral medications, vaginal suppositories, or injections. Progesterone supplements can help to support the pregnancy and prevent complications. It is important for women with low progesterone levels to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan.
In conclusion, low progesterone levels during pregnancy can have various effects on both the mother and the developing baby. It is important for women to be aware of the symptoms of low progesterone and seek medical attention if they experience any concerning signs. With proper treatment and monitoring, women with low progesterone can have a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Increased Risk of Miscarriage
Low levels of progesterone during pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage. Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. It helps to thicken the lining of the uterus, which is necessary for the implantation of the fertilized egg. It also helps to sustain the pregnancy by preventing the uterus from contracting and shedding its lining.
When progesterone levels are low, the risk of miscarriage can increase. This is because the uterus may not be able to support the growth and development of the embryo. Without adequate levels of progesterone, the uterus may contract and expel the embryo, leading to a miscarriage.
Low progesterone levels can also cause other symptoms that may indicate an increased risk of miscarriage. These symptoms may include spotting or bleeding, abdominal pain or cramping, and a decrease in pregnancy symptoms such as breast tenderness or morning sickness.
If you have low progesterone levels and are at an increased risk of miscarriage, your doctor may recommend progesterone supplementation. This can be done through oral medication, vaginal suppositories, or injections. Progesterone supplementation can help to support the pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
It is important to note that low progesterone levels are not always the cause of miscarriage. There can be other factors at play, such as chromosomal abnormalities or underlying health conditions. If you have experienced a miscarriage or are concerned about your fertility, it is important to speak with your doctor for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Developmental Issues in the Fetus
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can lead to several developmental issues in the fetus. Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. It helps prepare the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg and supports the growth and development of the fetus.
When progesterone levels are low, the fetus may not receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen needed for proper growth. This can result in developmental delays or abnormalities in various organs and systems, including the brain, heart, and lungs.
In some cases, low progesterone levels can increase the risk of miscarriage. Without adequate progesterone, the uterus may not be able to support the pregnancy, leading to the loss of the fetus.
It is important to recognize the symptoms of low progesterone levels during pregnancy, such as spotting or bleeding, abdominal pain, and decreased fetal movement. If these symptoms are present, it is essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for low progesterone levels may involve hormone supplementation, such as progesterone supplements or injections. These treatments can help maintain adequate progesterone levels and support a healthy pregnancy.
It is also important to note that low progesterone levels can impact fertility and make it more difficult to conceive. If you are planning to become pregnant and have a history of low progesterone levels, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss potential fertility treatments or interventions.
In conclusion, low progesterone levels during pregnancy can have significant developmental effects on the fetus. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical care is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and reducing the risk of miscarriage or developmental issues in the fetus.
FAQ about topic Understanding the Effects of Low Progesterone in Pregnancy
What is progesterone and why is it important during pregnancy?
Progesterone is a hormone produced by the ovaries during the menstrual cycle and by the placenta during pregnancy. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy by preparing the uterus for implantation and supporting the growth of the placenta. Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can lead to complications such as miscarriage or preterm birth.
What are the symptoms of low progesterone in pregnancy?
The symptoms of low progesterone in pregnancy can vary, but some common signs include spotting or bleeding, abdominal pain or cramping, and a decrease in breast tenderness. Other symptoms may include mood swings, fatigue, and difficulty sleeping. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other factors, so it is best to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
How is low progesterone in pregnancy diagnosed?
Low progesterone in pregnancy can be diagnosed through a blood test. The healthcare provider will measure the levels of progesterone in the blood to determine if they are within the normal range for pregnancy. In some cases, an ultrasound may also be performed to assess the health of the pregnancy and the development of the placenta.
Can low progesterone in pregnancy be treated?
Yes, low progesterone in pregnancy can be treated. The treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, progesterone supplements may be prescribed to help support the pregnancy. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress and getting enough rest, may also be recommended. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
What are the possible complications of low progesterone in pregnancy?
Low progesterone in pregnancy can increase the risk of complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, and gestational diabetes. It can also lead to a condition called preeclampsia, which is characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage. It is important for pregnant women with low progesterone levels to receive proper medical care and monitoring to help reduce the risk of these complications.
What are the effects of low progesterone in pregnancy?
Low progesterone in pregnancy can lead to a variety of effects, including an increased risk of miscarriage, preterm labor, and complications during pregnancy. It can also affect the development of the baby and increase the risk of birth defects.
I’m Diana Ricciardi, the author behind Makeitflip.com. My blog is a dedicated space for mothers and their kids, where I share valuable insights, tips, and information to make parenting a bit easier and more enjoyable.
From finding the best booster seat high chair for your child, understanding the connection between sciatica and hip pain, to exploring the benefits of pooping in relieving acid reflux, I cover a range of topics that are essential for every parent.
My goal is to provide you with practical advice and solutions that you can easily incorporate into your daily life, ensuring that you and your child have the best possible experience during these precious years.
